
Maria will repay the principal amount of debt plus interest @ 15% on April 30, 2021, on which the note payable will come due. The amount of interest payable on a balance sheet may be much critical from financial statement analysis perspective. For example, a higher than normal amount of unpaid interest signifies that the entity is defaulting on its debt liabilities. A higher interest liability may also impair the entity’s liquidity position in the eyes of its stakeholders. This journal entry is usually made at the period end adjusting entry to record the interest payable and expense when the interest payment on borrowings has not been made yet.
How To Calculate?
The difference in the stated rate and themarket rate determine the accounting treatment of the transactionsinvolving bonds. It becomes more complicated when the statedrate and the market rate differ. Before the bonds can be issued, theunderwriters perform many time-consuming tasks, including settingthe bond interest rate. A liability account that reports amounts received in advance of providing goods or services. When the goods or services are provided, this account balance is decreased and a revenue account is increased.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. This increases the net liability to $5,150, which represents the $5,000 proceeds from the note plus $150 of interest incurred since the inception of the loan. In Case 2, Notes Payable is credited for $5,200, the maturity value of the note, but S. The interest of $200 (12% of $5,000 for 120 days) is included in the face of the note at the time it is issued but is deducted from the proceeds at the time the note is issued. Each year, the unamortized discount is reduced by the interest expense for the year. This treatment ensures that the interest element is accounted for separately from the cost of the asset.
What Is the Difference Between Earned, Accrued, and Paid Interest on an Investment?
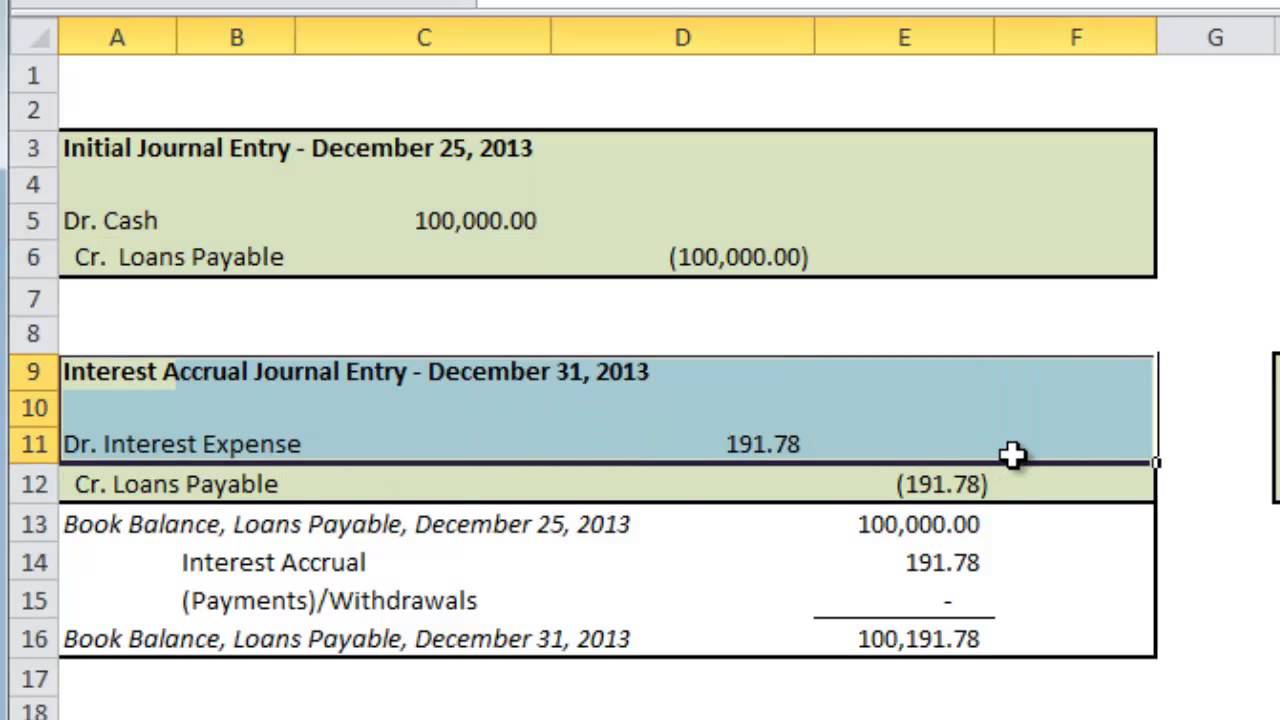
The piecharts below show the amount of the $1,073.64 payment allocated tointerest and loan reduction for the first and final payments,respectively, on the 30-year loan. Since the book value is equal to the amount that will be owed inthe future, no other account is included in the journal entry. In the what is a credit memo definition and how to create end, journal entries will total $150 worth of interest expense and interest payable. Loans and lines of credit accrue interest, which is a percentage on the principal amount of the loan or line of credit. The interest is a “fee” applied so that the lender can profit off extending the loan or credit.
- This method follows the matching principle of accounting, which states that revenues and expenses are recorded when they happen, instead of when payment is received or made.
- Interest Expense will be closed automatically at the end of each accounting year and will start the next accounting year with a $0 balance.
- The term is applicable to the unpaid interest expense up to the balance sheet date only; any amount of interest that relates to the period after balance sheet is not made part of the interest payable.
It is usually presented in “non-operating or other items section” which typically comes below the operating income. The interest payable account is classified as liability account and the balance shown by it up to the balance sheet date is usually stated as a line item under current liabilities section. If this journal entry is not made, the company’s total liabilities in the balance sheet as well as total expenses in the income statement will be understated by $3,000. Interest payable accounts are commonly seen in bond instruments because a company’s fiscal year end may not coincide with the payment dates.
Recording interest payable
Furthermore, this journal entry can be used to calculate the company’s interest rate. It is important for companies to ensure that all interest payable is reported accurately, as this can impact their credit score and their overall financial health. Failure to accurately report interest payable can lead to penalties imposed by the IRS. Therefore, companies must ensure that all interest payable is accurately reported on the balance sheet.
Entries to the general ledger for accrued interest, not received interest, usually take the form of adjusting entries offset by a receivable or payable account. Accrued interest is typically recorded at the end of an accounting period. The company can make the interest payable journal entry by debiting the interest expense account and crediting the interest payable account. For example, XYZ Company purchased a computer on January 1, 2016, paying $30,000 upfront in cash and with a $75,000 note due on January 1, 2019.
Except if the interest expense is paid in advance, the organization will always have to record interest payable in its balance sheets statements to report the interest paid to the lender. The most crucial part is that it is entirely different from interest expense. When a company borrows an amount from a financial institution, it must pay an interest expense. However, a company can’t show the entire amount of interest expense on the balance sheet. It can only show the interest amount that’s unpaid until the reporting date of the balance sheet.
If neither of these amounts can be determined, the note should be recorded at its present value, using an appropriate interest rate for that type of note. This situation may occur when a seller, in order to make a detail appear more favorable, increases the list or cash price of an item but offers the buyer interest-free repayment terms. A problem does arise, however, when an obligation has no stated interest or the interest rate is substantially below the current rate for similar notes. This entry records the $5,000 received for the accrued interest as a debit to Cash and a credit to Bond Interest Payable.
The effective interest rate (also called the yield) is the minimum rate of interest that investors accept on bonds of a particular risk category. The higher the risk category, the higher the minimum rate of interest that investors accept. The contract rate of interest is also called the stated, coupon, or nominal rate is the rate used to pay interest. Firms state this rate in the bond indenture, print it on the face of each bond, and use it to determine the amount of cash paid each interest period. Also, a higher interest liability may impair the entity’s liquidity position in the eyes of its stakeholders. At the end of the period, the company will have to recognize interest payable in the balance sheet and interest expenses in the income statement.
It’s important to calculate this rate before taking out a loan of any sort to make sure the business can afford to repay its debt. In most cases, you won’t have to calculate the interest due yourself – financial institutions will send you a breakdown of the cash owed. And if you’re using an online accounting system, the software can calculate this for you. The $1,500 balance in Wages Payable is the true amount not yet paid to employees for their work through December 31.
